Java Text Blocks
Java Text Blocks were officially introduced in Java 15 to make working with multi-line Strings easier and cleaner.
Before text blocks, writing HTML, SQL queries, JSON, or XML inside Java code required:
Escape sequences
Manual line breaks (
\n)Messy indentation
Hard-to-read code

Text Blocks solve all these problems using a triple-quoted syntax:
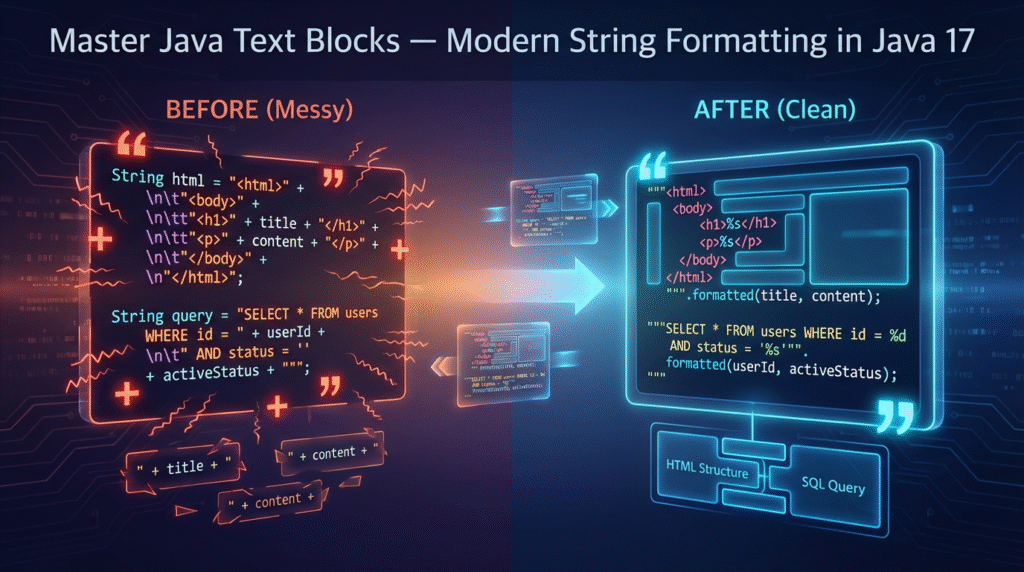
String html = """
<html>
<body>
<h1>Hello Text Blocks!</h1>
</body>
</html>
""";
Why Text Blocks Matter (My Personal Developer Experience)
When I worked on enterprise systems that generated HTML from Java code, I often wrote 20–30 line strings. Formatting them was painful:
One small indentation mistake → everything broke
Debugging was slow
Review comments were endless
Escape characters cluttered the code
After switching to Java Text Blocks:
✔ Code became cleaner
✔ Multi-line strings looked exactly like the final output
✔ Developers spent less time formatting, more time building
✔ Pull-requests were easier to reviewThis feature genuinely improves productivity.
Text Block Syntax
A Text Block always:
Starts with three double quotes (
""")Ends with three double quotes
Automatically handles line breaks & indentation
Example:
String message = """
Java Text Blocks
make your life easier!
""";
Output:
Java Text Blocks
make your life easier!
Key Benefits of Text Blocks
1. Cleaner Code
No need for \n, \", \\ or manual formatting.
2. Auto-Escaping
Most escape characters are not required anymore.
3. Better Readability
Your string looks exactly like the final output.
4. Ideal for Structured Data
Text Blocks work great with:
HTML
JSON
XML
SQL queries
Templates
Logs
Multi-line messages
Diagram: How Text Blocks Compare
+----------------------+---------------------------+
| Before Text Blocks | With Text Blocks |
+----------------------+---------------------------+
| Hard to read | Easy to read |
| Lots of escapes | Minimal escapes |
| Ugly indentation | Clean indentation |
| Extra debugging time | Faster development |
+----------------------+---------------------------+
Examples You Can Use in Real Projects
1. SQL Query Example
String query = """
SELECT id, name, salary
FROM employees
WHERE salary > 50000
ORDER BY salary DESC;
""";
2. JSON Response Example
String json = """
{
"name": "Shitanshu",
"role": "Java Developer",
"experience": 15
}
""";
3. HTML Template Example
String html = """
<html>
<body>
<h2>Welcome User</h2>
</body>
</html>
""";
4. Using formatted() With Text Blocks
Java allows template-style formatting:
String userTemplate = """
User ID: %d
Name: %s
Role: %s
""".formatted(101, "Shitanshu", "Engineer");
Text Blocks vs Traditional Strings
| Feature | Traditional Strings | Text Blocks |
|---|---|---|
| Clean layout | ❌ Hard | ✅ Easy |
| Escape characters | ❌ Required | ✅ Mostly unnecessary |
| Readability | ❌ Poor | ✅ Excellent |
| JSON/SQL/HTML | ❌ Difficult | ✅ Ideal |
| Code maintenance | ❌ Slow | ✅ Faster |
Common Mistakes (And Fixes)
❌ Misaligned indentation
✔ Fix by aligning the closing """ exactly where you want indentation to reset.
❌ Forgetting triple quotes
Always use:""" at the start and end.
❌ Adding spaces before closing quotes
This may add unwanted indentation.
Use Cases in Real-World Java Projects
API development → return JSON templates
Database apps → long SQL queries
Web applications → email & HTML templates
Cloud microservices → configuration payloads
Logging templates
Test data mocks
Text Blocks reduce manual formatting work and make code easier to maintain.
Best Practices
✔ Use Text Blocks for any multi-line structured string
✔ Keep indentation consistent
✔ Use .formatted() for template-style values
✔ Use them with logging frameworks to format logs
✔ Use descriptive variable names like emailTemplate, sqlQuery, htmlBody
FAQs — Java Text Blocks
1. Are text blocks available in older Java versions?
No. They were finalized in Java 15.
2. Can I use escape sequences inside text blocks?
Yes — but most are not needed.
3. Do text blocks support Unicode characters?
Absolutely.
4. Are text blocks faster?
Performance is similar, but development time is faster.
5. Can text blocks be used in Android?
Only if the Android toolchain supports Java 15+.
6. Will text blocks break indentation?
Only if closing quotes are misplaced.
7. Can I concatenate text blocks?
Yes:
String full = part1 + part2;
8. Do IDEs support syntax highlighting?
Yes — IntelliJ, Eclipse, VS Code.
9. Can I format values inside text blocks?
Yes, using .formatted() or String.format().
10. Can I store large HTML emails using text blocks?
Yes — this is one of the best uses.
Final Thoughts
Java Text Blocks make your code:
cleaner
easier to read
simpler to maintain
perfect for structured content
If you’re writing modern Java applications, switching to Text Blocks will improve your workflow immediately.
👉 Check out my guides on Java Lambda Expressions, Generics, and Pattern Matching.


Leave a Reply