API Gateway Pattern: Why Every Microservices System Needs an API Gateway
Microservices promise agility—but without control, they quickly turn into API chaos.
Imagine this:
A frontend app calling 10+ microservices
Each service has a different endpoint
Authentication logic duplicated everywhere
No centralized security
No rate limiting
No clean monitoring
This is where systems break, users feel latency, and teams burn out.
The API Gateway Pattern solves this problem by acting as a single, smart entry point into your microservices ecosystem.
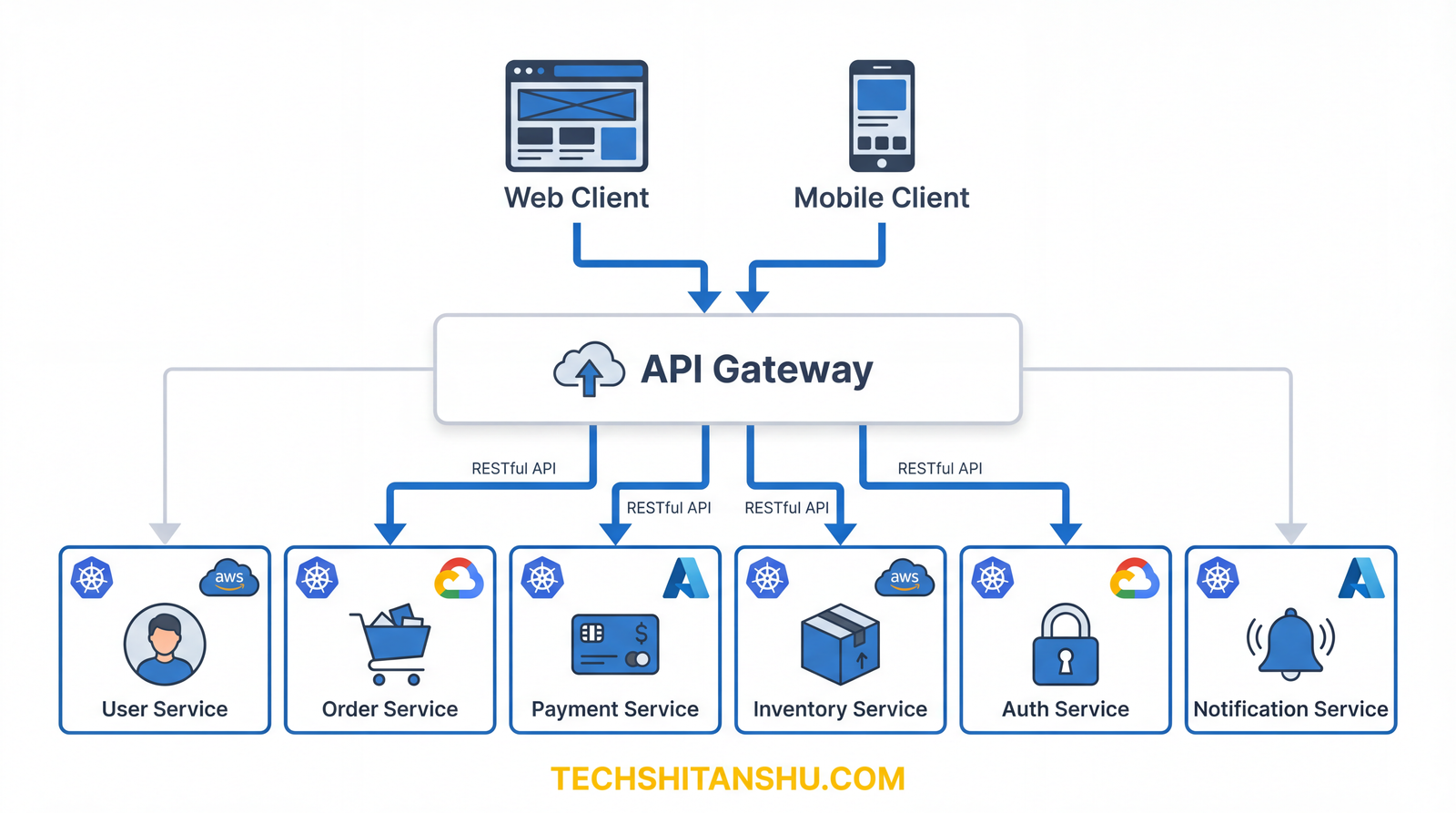
What Is the API Gateway Pattern?
The API Gateway Pattern introduces a dedicated layer that sits between clients and microservices.
Instead of clients calling services directly:
➡ They call the API Gateway
➡ The gateway routes requests to the right services
➡ Applies security, throttling, logging, and transformations
In Simple Words
The API Gateway is the front door of your microservices system.
Core Responsibilities of an API Gateway
An API Gateway is much more than routing.
Security & Authentication
OAuth2 / JWT validation
API keys
Centralized auth logic
Rate Limiting & Throttling
Protect services from overload
Prevent abuse & DDoS attacks
Request Routing
Route requests to correct microservice
Versioning support (v1, v2 APIs)
Aggregation
Combine responses from multiple services
Reduce frontend network calls
Observability
Central logging
Metrics
Tracing
High-Level API Gateway Architecture
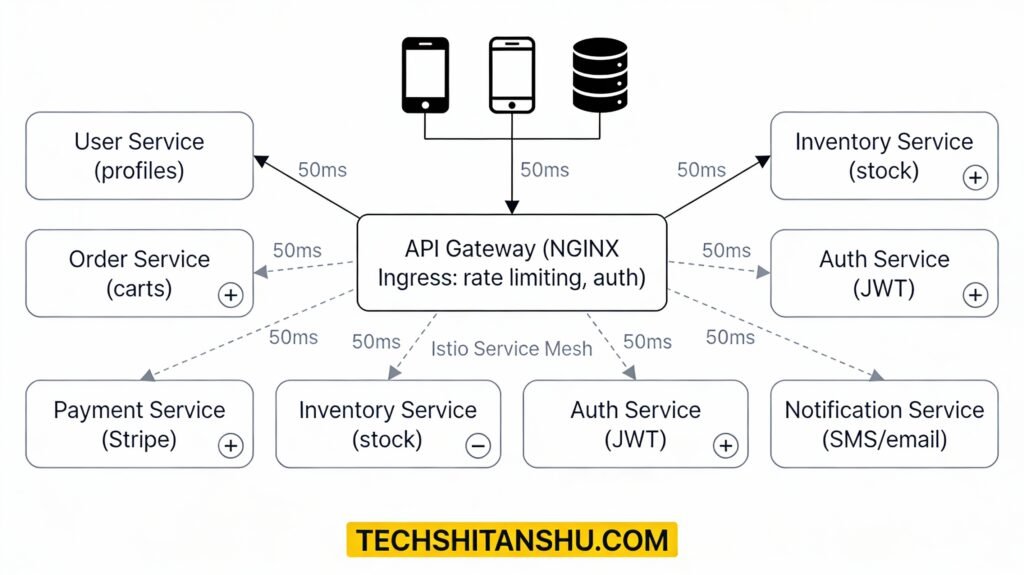
Why Direct Client-to-Service Calls Fail ❌
Without an API Gateway:
Frontend tightly couples with services
Security logic duplicated everywhere
Every UI change breaks APIs
Scaling becomes painful
👉 API Gateway = decoupling + control
API Gateway vs Load Balancer (Important for Interviews)
| Feature | API Gateway | Load Balancer |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | API management | Traffic distribution |
| Security | Yes | Limited |
| Auth | Built-in | No |
| Rate limiting | Yes | Rare |
| Aggregation | Yes | No |
👉 They complement, not replace each other.
API Gateway vs Backend for Frontend (BFF)
API Gateway
One gateway for all clients
Shared logic
BFF Pattern
One gateway per client (Web, Mobile)
Tailored APIs
👉 Many large systems use API Gateway + BFF together.
Popular API Gateway Tools (Real-World)
Open Source
Spring Cloud Gateway
Kong
NGINX
Traefik
Cloud-Managed
AWS API Gateway
Azure API Management
Google Cloud API Gateway
API Gateway in AWS (Practical View)
AWS API Gateway integrates with:
Lambda (Serverless)
EC2 / ECS
EKS (Kubernetes)
Cognito (Auth)
CloudWatch (Logs & metrics)
Common API Gateway Patterns (Advanced)
🔁 Request Aggregation Pattern
One request → multiple services → single response
🔄 Protocol Translation
REST → gRPC
REST → GraphQL
🧪 Canary Releases
Route small % traffic to new versions
Real world example API Gateway Patterns
The API Gateway Service is a key component in the Event-Sourcing + CQRS example application provided in the cer/event-sourcing-examples repository on GitHub. This project demonstrates how to build a microservices architecture driven by Event Sourcing, CQRS (Command Query Responsibility Segregation), and powered by Spring Boot and Docker.
What Is This Example Application?
This repository provides a complete example application illustrating how modern distributed systems can be built using microservices, event-driven architecture, event sourcing, and CQRS. The application models a money transfer system (similar to a banking domain) where users can create customers, create accounts, and transfer money.
Multiple independent services make up the application:
Customers Service — for creating and managing customers
Accounts Service — for account creation and management
Transactions Service — to manage money transfers
View Services — read-optimized services for views of customers/accounts
…and finally the API Gateway Service, which acts as the façade in front of all other services.
What Is the API Gateway Service?
The API Gateway Service is a Spring Boot-based application whose primary role is to act as a single entry point for clients (like front-end applications or API consumers) to interact with the entire microservices ecosystem.
In microservices architecture, the API Gateway:
✅ Provides a unified REST endpoint
✅ Routes requests to the appropriate downstream services
✅ Helps abstract service boundaries from clients
✅ Simplifies client logic by providing a consolidated API layer
In this example, the gateway acts as a Facade — encapsulating how internal services are composed and accessed.
Why Use an API Gateway Here?
Modern microservices introduce complexity:
Many independent services
Each service can have its own API endpoints
Services might evolve independently
An API Gateway centralizes:
✔ Routing
✔ Load balancing
✔ Potential cross-cutting concerns like authentication, logging, metrics (in more advanced setups)
It ensures clients don’t have to call individual microservices directly — they only talk to one gateway layer.
⚙️ How the API Gateway Fits With Event Sourcing & CQRS
To understand the gateway’s purpose in context:
🧩 Event Sourcing
Instead of persisting current state in a database, systems store every business change as events — immutable facts about what happened. This enables powerful capabilities like event replay, audit trails, and temporal queries.
🧩 CQRS
Read and write operations are separated:
Writes (Commands) affect state and generate events
Reads (Queries) are served from optimized “view” databases or projections
The API Gateway directs clients to appropriate endpoints based on the type of request — whether it’s for write operations or retrieving read models.
Typical Responsibilities of the API Gateway in This Project
While the specific source files in the api-gateway-service folder weren’t fully visible from the link, an API Gateway in such a project commonly includes:
🔹 Routing Configuration
A set of routes that map external API endpoints to internal services (e.g., customer service, account service, transaction service).
🔹 HTTP Controller Endpoints
Controllers that expose REST APIs such as:
POST /customers
GET /customers/{id}
POST /accounts
GET /accounts/{id}
POST /transactions
Clients invoke these gateway APIs instead of calling each service directly. The gateway then proxies the requests internally.
🔹 Fallbacks and Resiliency
Gateways often integrate with patterns like:
Circuit Breakers
Timeouts
Fallback responses
Though not always in simple examples, these improve fault tolerance in distributed systems.
🔹 Response Aggregation
In some setups, the gateway may combine responses from multiple microservices into one response for the client. This simplifies client logic.
Running the Entire Example
To run the entire application:
Build the project using Gradle.
Launch all services together using Docker Compose.
The API Gateway starts and provides access to the whole system. Usually this is on port
8080(configurable).Open a browser or use a REST client to send requests to the gateway — it will route them internally.
In Summary
What the API Gateway Service Does
✔ Acts as the front door to the entire application
✔ Routes client requests to the correct microservices
✔ Hides internal service complexity
✔ Makes interaction with the event-sourced system simple
✔ Helps support a scalable microservices architecture powered by Spring Boot
In essence, in this event-sourcing + CQRS microservices application, the API Gateway service improves modularity, reduces coupling for clients, and supports clean architectural separation
Performance Considerations
Yes, API Gateway adds a hop—but:
Caching improves speed
Aggregation reduces calls
Central throttling prevents overload
👉 Net result: better performance
Anti-Patterns to Avoid
❌ Business logic in gateway
❌ Overloading gateway with heavy computation
❌ Single gateway without HA
❌ Ignoring gateway monitoring
Best Practices (Production-Ready)
✔ Keep gateway thin
✔ Use JWT & OAuth centrally
✔ Enable caching
✔ Run in high availability
✔ Combine with Service Discovery + Circuit Breaker
API Gateway + Service Discovery (Perfect Pair)
Gateway discovers services dynamically
No hardcoded IPs
Seamless scaling
👉 This links perfectly to your Service Discovery Pattern article.
Security Benefits (Big Reason Enterprises Use It)
Single attack surface
Centralized WAF
API key management
Request validation
This alone justifies the pattern in regulated systems.
Real-World Use Case
E-commerce platform
Web + Mobile clients
15+ microservices
One API Gateway
Auth, rate limit, logging centralized
Result:
✔ Faster frontend
✔ Fewer bugs
✔ Easier scaling
FAQs
❓ Is API Gateway mandatory in microservices?
Not mandatory—but strongly recommended for production systems.
❓ Does API Gateway slow down requests?
Slightly, but caching and aggregation usually improve overall performance.
❓ Can API Gateway replace service discovery?
No. It often uses service discovery internally.
❓ Is API Gateway only for microservices?
Mostly yes—but it’s also useful for serverless APIs.
❓ Which API Gateway is best?
Spring apps → Spring Cloud Gateway
AWS → AWS API Gateway
Kubernetes → Kong / NGINX
Part of our complete Microservices Design Patterns Series.

Leave a Reply