What Is Spring AI? Architecture, Components & Why It Exists
Generative AI adoption in Java didn’t fail because of missing APIs.
It failed because enterprise systems need structure, not scripts.
For years, Java teams integrated AI by:
Calling external Python services
Writing thin REST wrappers over LLM APIs
Treating AI as a black-box dependency
That approach breaks down fast in production.
Spring AI exists because enterprise AI needs the same discipline Java systems already have — configuration, security, observability, testing, and architectural consistency.
This article explains what Spring AI is, how it’s architected, and why it exists, without marketing noise or framework worship.
Why Spring AI Had to Exist
Before Spring AI, Java teams faced a familiar pattern:
LLM APIs exposed as raw HTTP calls
Prompt strings hardcoded in services
No consistent abstraction for:
Chat models
Embeddings
Vector stores
No observability into AI calls
No governance around prompts or usage
This created:
Fragile systems
Vendor lock-in
Security risks
Unpredictable costs
Spring AI was created to answer one core question:
How do we make Generative AI a first-class, production-grade backend capability in Java?
What Is Spring AI
Spring AI is a Spring framework module that provides consistent, enterprise-ready abstractions for working with Large Language Models, embeddings, and vector databases inside Spring applications.
It is not:
A low-level SDK
A chatbot framework
A replacement for AI providers
It is:
An integration and architecture framework
Designed for Spring Boot, Spring Cloud, and enterprise Java
Spring AI vs “Just Calling an LLM API”
Calling an LLM directly looks easy — until it isn’t.
| Direct LLM Calls | Spring AI |
|---|---|
| Hardcoded prompts | Structured prompts |
| Vendor-specific APIs | Provider-agnostic abstractions |
| No retries or fallbacks | Resilience patterns |
| No observability | Metrics & tracing |
| Tight coupling | Clean architecture |
Spring AI doesn’t make AI smarter.
It makes AI usage safer, cleaner, and scalable.
Core Design Philosophy of Spring AI
Spring AI follows the same principles that made Spring successful:
1️⃣ Abstraction Without Hiding Reality
You still understand tokens, prompts, and models — but you don’t couple your system to one vendor.
2️⃣ Convention Over Configuration
AI components integrate like any other Spring bean.
3️⃣ Production First
Security, monitoring, configuration, and testing are first-class concerns.
4️⃣ Architecture > Prompt Tricks
Spring AI encourages system design, not prompt hacks.
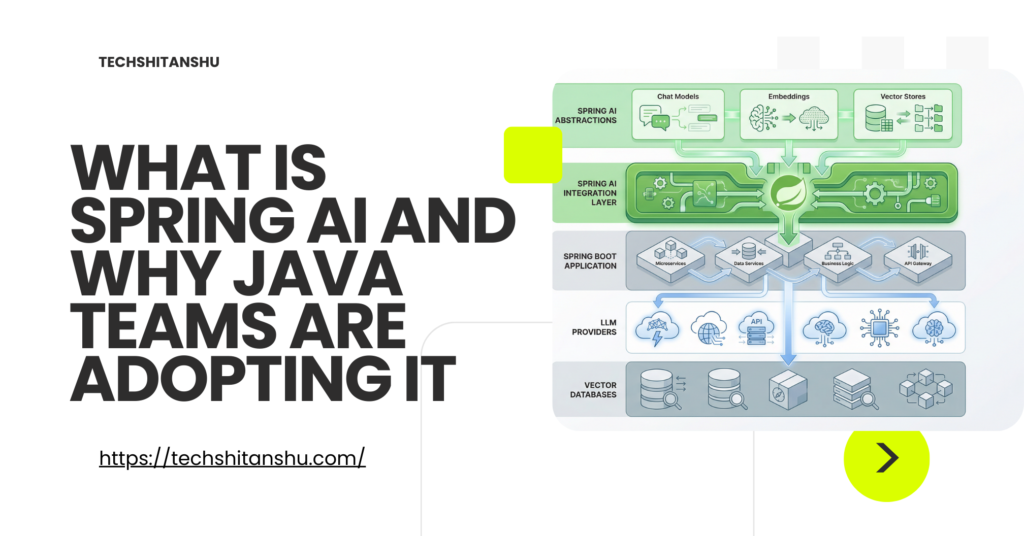
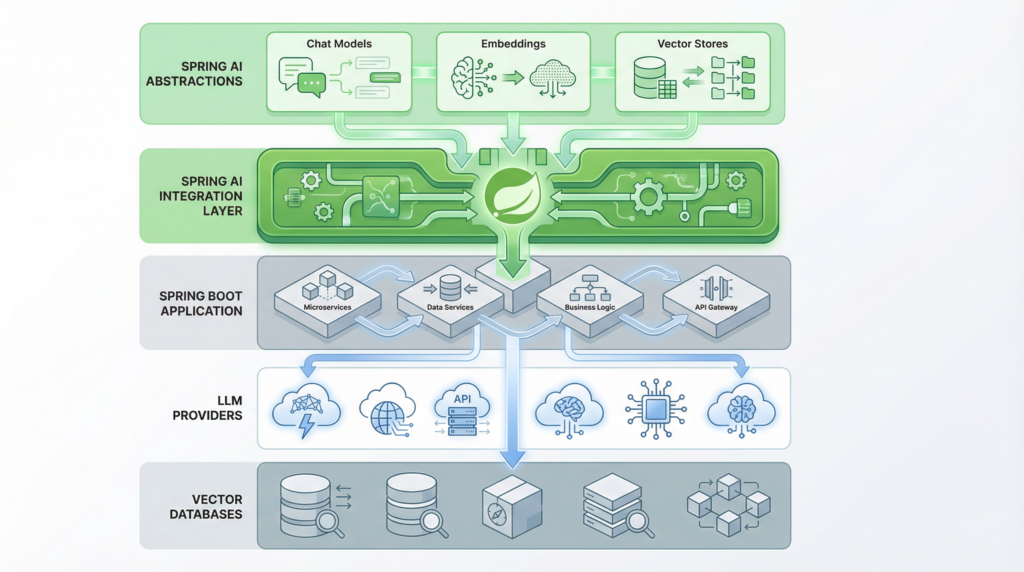
High-Level Spring AI Architecture
At a conceptual level, Spring AI sits between your application and AI providers.
Spring Boot Application
↓
Spring AI Abstractions
↓
LLMs / Embeddings / Vector Stores
↓
AI Providers (OpenAI, Azure, Local Models)
Your application talks to interfaces.
Providers can change. Architecture remains stable.
Core Components of Spring AI
Understanding these components is essential — especially for interviews and system design.
1️⃣ ChatModel
The ChatModel abstraction represents an LLM capable of generating responses.
From a backend perspective:
It’s similar to a service client
But non-deterministic
Token-based
Cost-sensitive
Spring AI standardizes:
Input prompts
Output handling
Provider differences
This prevents your business logic from depending on one AI vendor.
2️⃣ Prompt
Prompts in Spring AI are not raw strings.
They are:
Structured
Template-driven
Parameterized
Testable
Think of prompts as:
Configuration + business intent, not user input.
This allows:
Version control
Safer modifications
Better governance
3️⃣ EmbeddingModel
Embeddings convert text into vectors.
Spring AI abstracts embedding generation so you can:
Swap providers
Standardize preprocessing
Centralize configuration
This is critical for:
Semantic search
RAG systems
Recommendation engines
4️⃣ VectorStore
The VectorStore abstraction represents vector databases like:
Pinecone
Weaviate
Milvus
PostgreSQL (PGVector)
Spring AI allows you to:
Store embeddings
Perform similarity search
Retrieve context for LLMs
This is the foundation for Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG).
5️⃣ Model Clients & Providers
Spring AI supports multiple providers:
Cloud LLMs
Managed services
Local models
The key idea:
Your system depends on Spring AI interfaces, not provider SDKs.
This avoids vendor lock-in — a major enterprise concern.
Why Spring AI Matters for Backend Architecture
Spring AI shifts how AI is designed, not just used.
❌ Old Model
AI as an external service called ad-hoc.
✅ New Model
AI as a backend component with:
Lifecycle
Monitoring
Security
Cost controls
This aligns AI with:
Microservices
Event-driven systems
API gateways
Platform engineering
Spring AI vs LangChain (Quick Perspective)
This is not a competition — it’s a difference in intent.
| LangChain | Spring AI |
|---|---|
| Python-first | Java-first |
| Experimentation | Production systems |
| Script-friendly | Architecture-friendly |
| Research workflows | Enterprise workflows |
Spring AI is built for:
Java teams
Long-lived systems
Compliance and governance
Platform consistency
Common Misunderstandings About Spring AI
❌ “Spring AI replaces AI providers”
✅ It integrates them safely
❌ “Spring AI hides AI complexity”
✅ It exposes it responsibly
❌ “Spring AI is only for chatbots”
✅ It’s for backend AI systems
❌ “It’s too heavy for small apps”
✅ It scales down as well as up
When You Should (and Shouldn’t) Use Spring AI
✅ Use Spring AI if:
You’re building AI features in Spring Boot
You care about maintainability
You expect change in AI providers
You need observability and security
❌ Don’t use Spring AI if:
You’re prototyping throwaway scripts
You only need one static API call
You don’t plan to maintain the system
How Spring AI Fits Into the Bigger Picture
Spring AI is not the end goal.
It enables:
AI-powered APIs
RAG systems
AI microservices
Secure enterprise assistants
It integrates naturally with:
Spring Security
Spring Cloud
Observability stacks
Container platforms
This is why it exists.
What’s Next in the Series
Now that you understand why Spring AI exists, the next step is how it’s used.
👉 Building Generative AI Applications with Spring Boot
We’ll move from architecture to real application flows — APIs, chat systems, and AI-powered services.
FAQ – Frequently Asked Questions
❓ What is Spring AI used for?
Spring AI is used to integrate Generative AI capabilities such as large language models, embeddings, and vector databases into Spring Boot applications using consistent, production-ready abstractions suitable for enterprise systems.
❓ Is Spring AI a replacement for OpenAI or other LLM providers?
No. Spring AI does not replace AI providers. It acts as an integration layer that standardizes how Spring applications interact with different LLMs, embedding models, and vector stores without locking the system to a single vendor.
❓ How is Spring AI different from calling an LLM API directly?
Calling an LLM API directly couples your application to a specific provider and lacks structure. Spring AI provides abstractions, configuration management, observability, and architectural consistency, making AI usage safer and more maintainable in production systems.
❓ Does Spring AI support Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG)?
Yes. Spring AI includes abstractions for embeddings and vector stores, which are essential for building RAG systems that retrieve relevant documents before generating responses with an LLM.
❓ Is Spring AI suitable for microservices architecture?
Yes. Spring AI integrates naturally with Spring Boot and Spring Cloud, making it suitable for microservices-based architectures where AI is treated as a backend system component rather than a standalone feature.
❓ Do I need machine learning knowledge to use Spring AI?
No. Spring AI is designed for Java and Spring developers. You only need to understand Generative AI concepts, prompt behavior, and system design considerations, not machine learning algorithms.
Final Thought
Spring AI doesn’t make Java developers “AI engineers”.
It makes them responsible system designers in an AI-enabled world.
And that’s exactly what modern backend systems require.
Generative AI with Spring: Complete Java Developer & Architect Series

Leave a Reply