Backend for Frontend Pattern
Introduction: Why Backend for Frontend (BFF) Matters Today
Modern applications no longer have a single frontend.
Today, most products support:
Web applications
Mobile apps (iOS & Android)
Tablets, smart TVs, IoT devices
Partner and third-party integrations
Each frontend has different data needs, performance constraints, and UX expectations.
That’s where the Backend for Frontend pattern (BFF) shines.
Instead of forcing one generic backend to serve everyone, BFF creates dedicated backends optimized for each frontend experience.
What Is the Backend for Frontend Pattern(BFF)?
Backend for Frontend (BFF) is a microservices design pattern where each frontend has its own backend service tailored specifically for its needs.
Simple Definition
One frontend → One backend optimized just for it.
Example
| Frontend | BFF |
|---|---|
| Web App | Web BFF |
| Mobile App | Mobile BFF |
| Admin Panel | Admin BFF |
Each BFF:
Aggregates data from multiple microservices
Shapes responses exactly how the frontend needs
Handles authentication, authorization, and caching
Why Traditional APIs Fail at Scale
Traditional architectures usually expose:
One REST API
One GraphQL endpoint
One “one-size-fits-all” backend
Problems This Creates
Over-fetching or under-fetching data
Slow mobile performance
Complex frontend logic
Frequent breaking changes
Security risks due to overexposed APIs
As systems scale, this approach becomes fragile and expensive.
How BFF Architecture Works
High-Level Flow
Frontend sends request to its dedicated BFF
BFF calls multiple internal microservices
BFF aggregates, filters, and formats data
Optimized response is returned to frontend
Key Idea
Frontends never talk directly to core microservices
Core Components of a BFF Architecture
1. Frontend Applications
Web
Mobile
Desktop
Admin dashboards
2. BFF Layer
One BFF per frontend
Lightweight and focused
Acts as a facade
3. Microservices
User Service
Order Service
Payment Service
Inventory Service
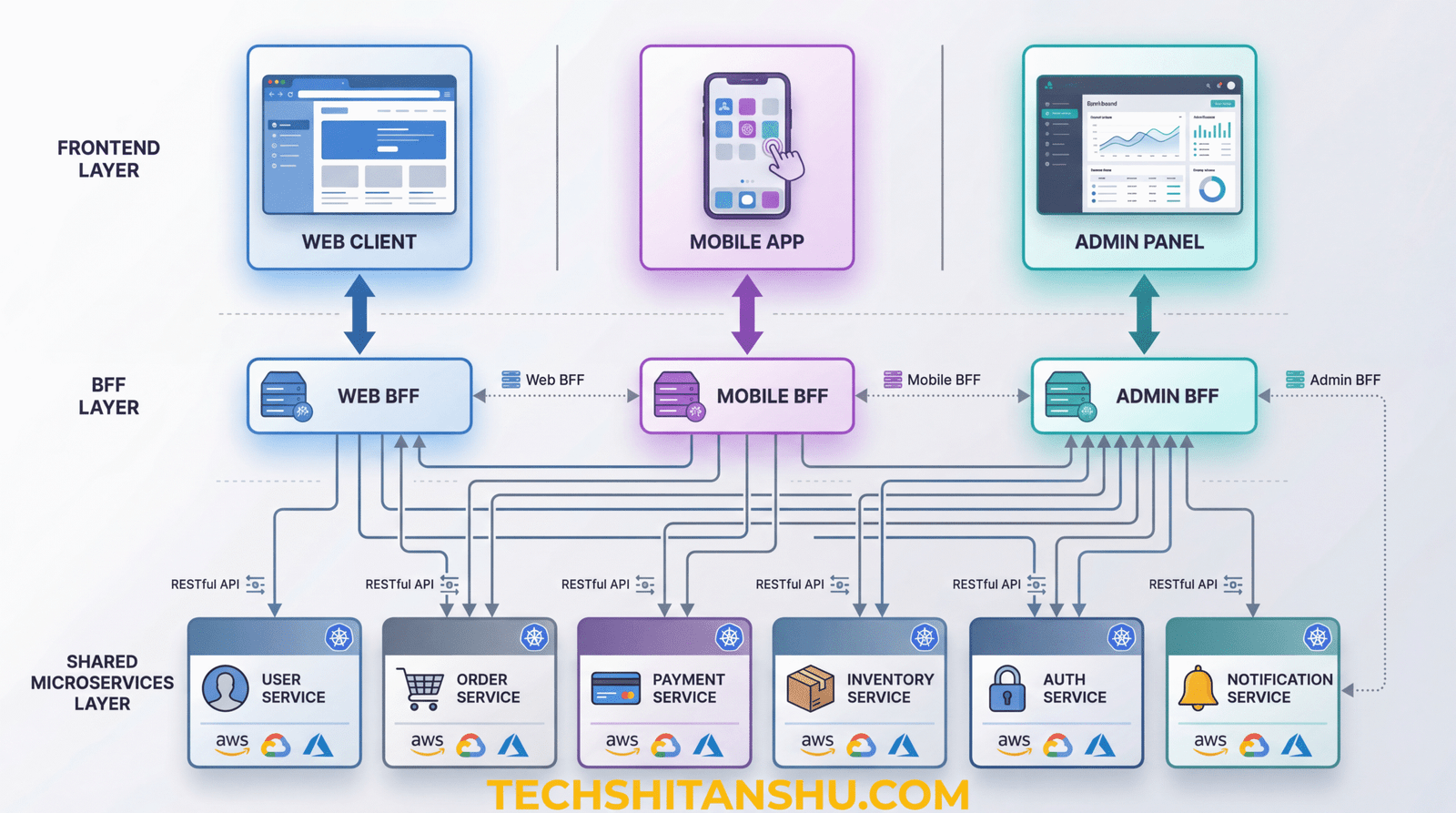
Real-World Example: E-Commerce Platform
Without BFF
Mobile app fetches unnecessary data
Web app struggles with performance
Backend changes break all clients
With BFF
Mobile BFF returns lightweight JSON
Web BFF includes rich UI data
Admin BFF exposes detailed analytics
Result:
✅ Faster apps
✅ Happier users
✅ Fewer production bugs
Benefits of Backend for Frontend Pattern
1. Performance Optimization (High CPC Topic)
Each frontend receives exactly what it needs, nothing more.
2. Cleaner Frontend Code
No more complex data transformation logic in UI layers.
3. Faster Development Cycles
Frontend and backend teams move independently.
4. Improved Security
Expose only necessary APIs per frontend.
5. Better Scalability
Scale BFFs independently based on traffic.
Drawbacks of BFF Pattern (Be Honest for SEO)
1. Increased Number of Services
More services to deploy and monitor.
2. Duplication Risk
Similar logic across multiple BFFs.
3. Operational Complexity
Requires strong DevOps and observability.
💡 Best Practice: Keep BFFs thin. Business logic belongs in core services.
Backend for Frontend vs API Gateway
| Feature | BFF | API Gateway |
|---|---|---|
| Frontend-Specific | ✅ Yes | ❌ No |
| Business Logic | Light | Minimal |
| Custom Responses | High | Limited |
| Scaling | Per frontend | Centralized |
👉 Best Approach:
Use API Gateway + BFF together for enterprise systems.
BFF vs GraphQL
GraphQL reduces over-fetching, but:
Still exposes backend schema
Requires frontend query expertise
Can create security risks
BFF:
Offers controlled, curated APIs
Easier governance for enterprises
When Should You Use BFF?
Use BFF if:
You have multiple frontends
Performance matters
Teams work independently
You’re building SaaS or cloud-native platforms
Avoid BFF if:
You have only one frontend
Small monolithic application
Technologies Commonly Used for BFF
High-CPC cloud keywords advertisers love:
Node.js
Spring Boot
NestJS
AWS Lambda
Azure Functions
Kubernetes
Docker
API Gateway
OAuth 2.0 / OpenID Connect
Best Practices for BFF Design
✔ Keep BFF logic thin
✔ Avoid database access from BFF
✔ Use caching aggressively
✔ Secure with proper IAM roles
✔ Monitor latency and errors
Your frontend doesn’t need everything — it needs the right backend.
That’s where the Backend for Frontend (BFF) Pattern shines 👇
✔️ Faster APIs for web & mobile
✔️ Cleaner microservices architecture
✔️ Better security & performance
✔️ Happier frontend teams 😄
If you’re building scalable microservices, this pattern can completely change how your APIs perform.
Backend for Frontend (BFF) Pattern Explained Perfect for:
Backend & Full-Stack Developers
System Architects
Startup & Enterprise Engineering Teams
FAQs
What is Backend for Frontend (BFF)?
Backend for Frontend is a design pattern where each frontend application has its own dedicated backend tailored to its needs.
Is BFF suitable for microservices?
Yes, BFF works best with microservices by acting as a façade between frontend and backend services.
Does BFF replace API Gateway?
No. BFF complements API Gateway rather than replacing it.
Is BFF expensive?
Initially yes, but it reduces long-term development and maintenance costs.
Is BFF better than GraphQL?
For enterprise security and governance, BFF often provides better control than GraphQL.
Final Thoughts
The Backend for Frontend pattern is no longer optional for modern applications—it’s a strategic necessity.
If you’re building:
SaaS platforms
Cloud-native systems
High-traffic enterprise apps
BFF helps you deliver speed, security, and scalability—all while improving developer productivity.
“Part of our Microservices Design Patterns Series.”

Leave a Reply