Circuit Breaker Pattern in Microservices: Build Fault-Tolerant, Resilient Systems That Don’t Collapse Under Failure (2026)
The Circuit Breaker pattern helps protect a system from repeatedly calling a failing service. Instead of letting requests pile up and make things worse, it “breaks the circuit” after detecting repeated failures and temporarily stops the calls. This gives the failing service time to recover while preventing the entire system from slowing down or crashing. Once things look healthy again, the circuit allows requests to flow normally. In simple terms, it’s like an automatic safety switch that keeps your microservices stable under stress.
Introduction: Why Microservices Fail (And Why That’s Dangerous )
Failures are normal in distributed systems.
What’s dangerous is how failures spread.
Picture this:
Service A calls Service B
Service B is slow or down
Threads pile up
Service A becomes unresponsive
Entire system starts failing
This is called a cascading failure — and it has taken down some of the biggest platforms in the world.
The Circuit Breaker Pattern exists to stop this exact nightmare.
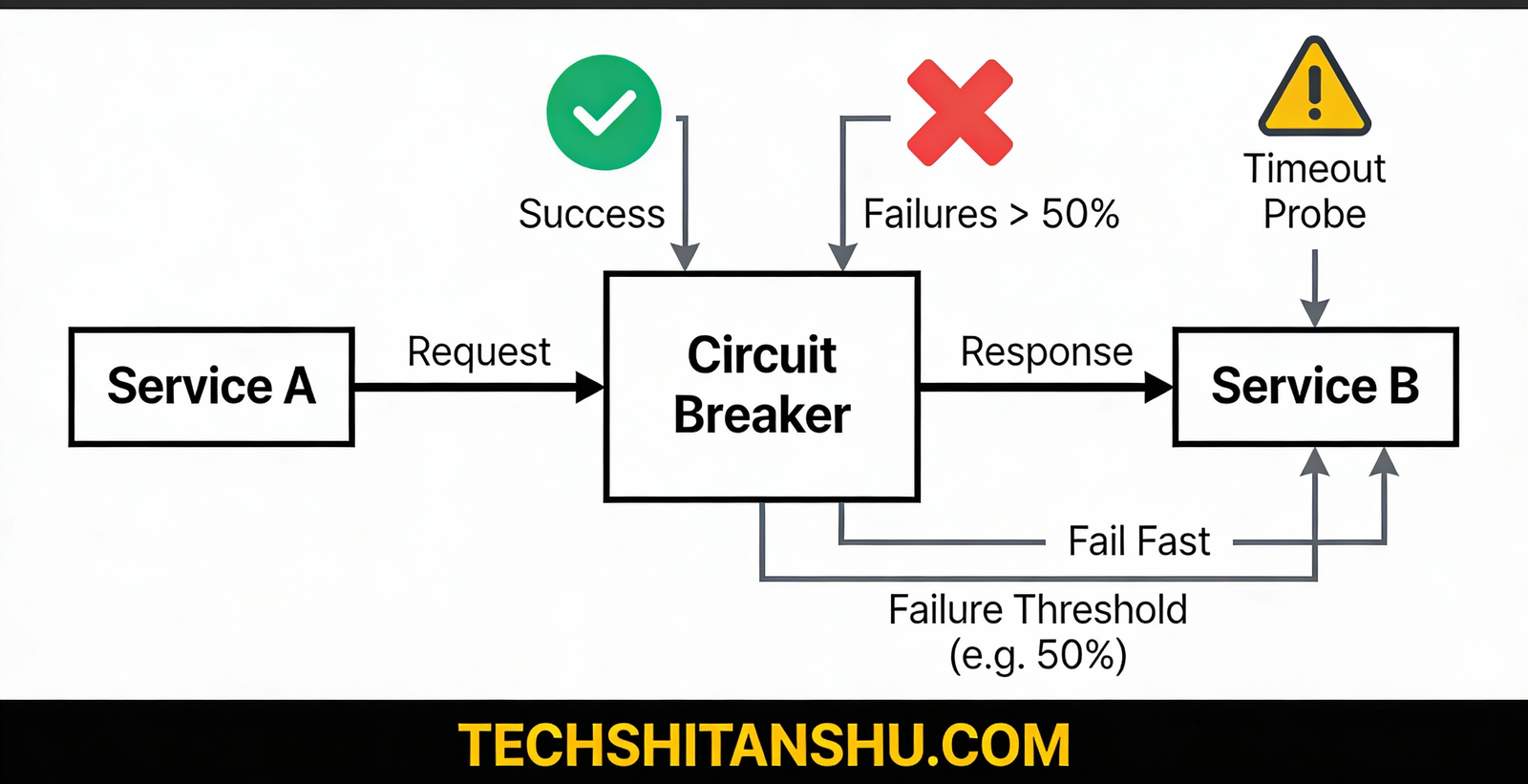
What Is the Circuit Breaker Pattern?
The Circuit Breaker Pattern prevents a microservice from repeatedly calling another service that is failing or slow.
Instead of waiting endlessly:
It detects failures
Stops calls temporarily
Allows the system to recover gracefully
Simple Analogy ⚡
Think of your home’s electrical circuit breaker:
Too much load → breaker trips
Power stops
Damage is avoided
Same logic. Different system.
Why Circuit Breakers Are Critical in Microservices
In microservices:
Network calls are unreliable
Latency is unpredictable
Failures are inevitable
Without circuit breakers:
❌ Threads get exhausted
❌ Latency explodes
❌ User experience crashes
With circuit breakers:
✅ Fail fast
✅ Protect resources
✅ Recover automatically
Circuit Breaker States (Very Important)
1️⃣ Closed State (Normal Mode)
Requests flow normally
Failures are monitored
2️⃣ Open State (Failure Mode)
Requests are blocked
Calls fail immediately
Fallback logic executes
3️⃣ Half-Open State (Recovery Mode)
Limited test requests allowed
If successful → close circuit
If failures continue → reopen
What Problems Does Circuit Breaker Solve?
✔ Prevents cascading failures
✔ Avoids thread pool exhaustion
✔ Improves system stability
✔ Enables graceful degradation
Circuit Breaker vs Retry Pattern
| Feature | Circuit Breaker | Retry |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Stop calls | Repeat calls |
| Failure handling | Fail fast | Increase load |
| Best use | Prolonged failures | Transient errors |
👉 Never use retries alone without a circuit breaker.
Circuit Breaker + Service Discovery + API Gateway
The perfect trio:
- Service Discovery → finds services
- API Gateway → controls access
- Circuit Breaker → handles failures
This trio is the backbone of resilient architectures.
Popular Circuit Breaker Tools
Java / Spring Ecosystem
- Resilience4j (Recommended)
- Sentinel
- Spring Cloud Circuit Breaker
Cloud / Platform Level
- Istio (Service Mesh)
- AWS App Mesh
- Envoy Proxy
👉 Modern systems prefer library + service mesh combo.
Circuit Breaker with Resilience4j (Example)
Human translation:
If 50% calls fail → open circuit
Wait 10 seconds before retry
Monitor last 10 calls
CircuitBreakerConfig config = CircuitBreakerConfig.custom()
.failureRateThreshold(50)
.waitDurationInOpenState(Duration.ofSeconds(10))
.slidingWindowSize(10)
.build();
Fallback Strategies (User Experience Saver)
When the circuit is open, fallbacks matter.
Examples:
Return cached data
Show partial response
Graceful error message
Static default response
A fast fallback is better than a slow failure.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
❌ Using circuit breaker everywhere blindly
❌ No fallback logic
❌ Poor threshold tuning
❌ Ignoring monitoring & metrics
❌ Mixing business logic with resilience logic
Best Practices (Production-Proven)
✔ Combine with timeouts
✔ Tune thresholds carefully
✔ Monitor state changes
✔ Keep fallback logic simple
✔ Test failure scenarios
Real-World Use Case
Payment Service
External payment gateway is unstable
Circuit breaker opens after failures
Orders temporarily switch to COD
System stays online
Result:
✔ Zero downtime
✔ Better user trust
✔ Controlled failure
Circuit Breaker in Kubernetes & Cloud
Often implemented via service mesh
No code changes required
Centralized observability
Platform-level resilience
This is why cloud-native systems love this pattern.
FAQs
❓ Is Circuit Breaker mandatory in microservices?
For production systems—yes, especially when services depend on each other.
❓ What’s better: Hystrix or Resilience4j?
Hystrix is deprecated. Resilience4j is the modern choice.
❓ Can API Gateway act as a circuit breaker?
Yes, many gateways support it—but internal service-to-service calls still need protection.
❓ Does circuit breaker improve performance?
Indirectly, yes—by avoiding slow failures and resource exhaustion.
❓ Where should circuit breaker be implemented?
At service boundaries, especially when calling remote services.
Link to:
Service Discovery Pattern
Microservices Design Patterns (Pillar Article)
Anchor:
“This is part of our complete Microservices Design Patterns Series.”

Leave a Reply