Enterprise Data Warehouse (EDW) Architecture – A Complete Guide
In today’s data-driven world, data is the backbone of every enterprise decision. But raw data alone doesn’t create value — organized, trusted, and accessible data does.
This is where Enterprise Data Warehouse (EDW) architecture becomes critical.
An EDW acts as the single source of truth for an organization, bringing together data from multiple systems, cleaning it, organizing it, and making it ready for analytics, reporting, and AI-driven insights.
In this guide, we’ll break down EDW architecture step by step, using simple language, real-world examples, and best practices that enterprises actually use.
What Is an Enterprise Data Warehouse (EDW)?
An Enterprise Data Warehouse is a centralized repository that stores structured and semi-structured data from across an organization.
It is designed to:
-
Support business intelligence (BI)
-
Enable historical analysis
-
Power dashboards, reports, and AI models
-
Ensure data consistency and governance
Unlike operational databases (OLTP systems), EDWs are optimized for analytics, not transactions.
Why EDW Architecture Matters
Without a strong architecture:
-
Reports don’t match
-
Data becomes unreliable
-
Performance degrades
-
Compliance risks increase
A well-designed EDW architecture ensures:
✔ High performance
✔ Scalability
✔ Data accuracy
✔ Governance & security
✔ Faster decision-making
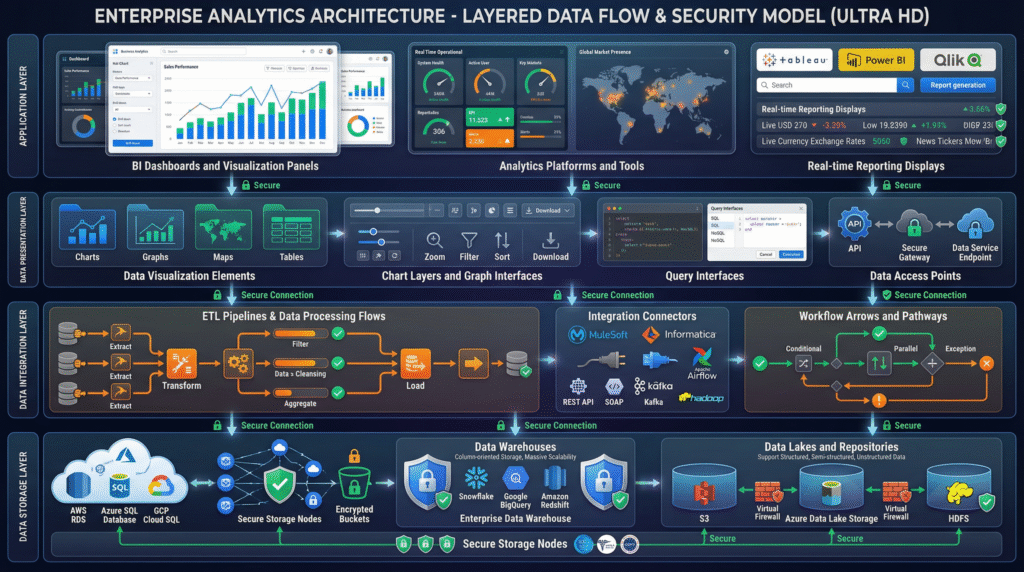
Core Layers of Enterprise Data Warehouse Architecture
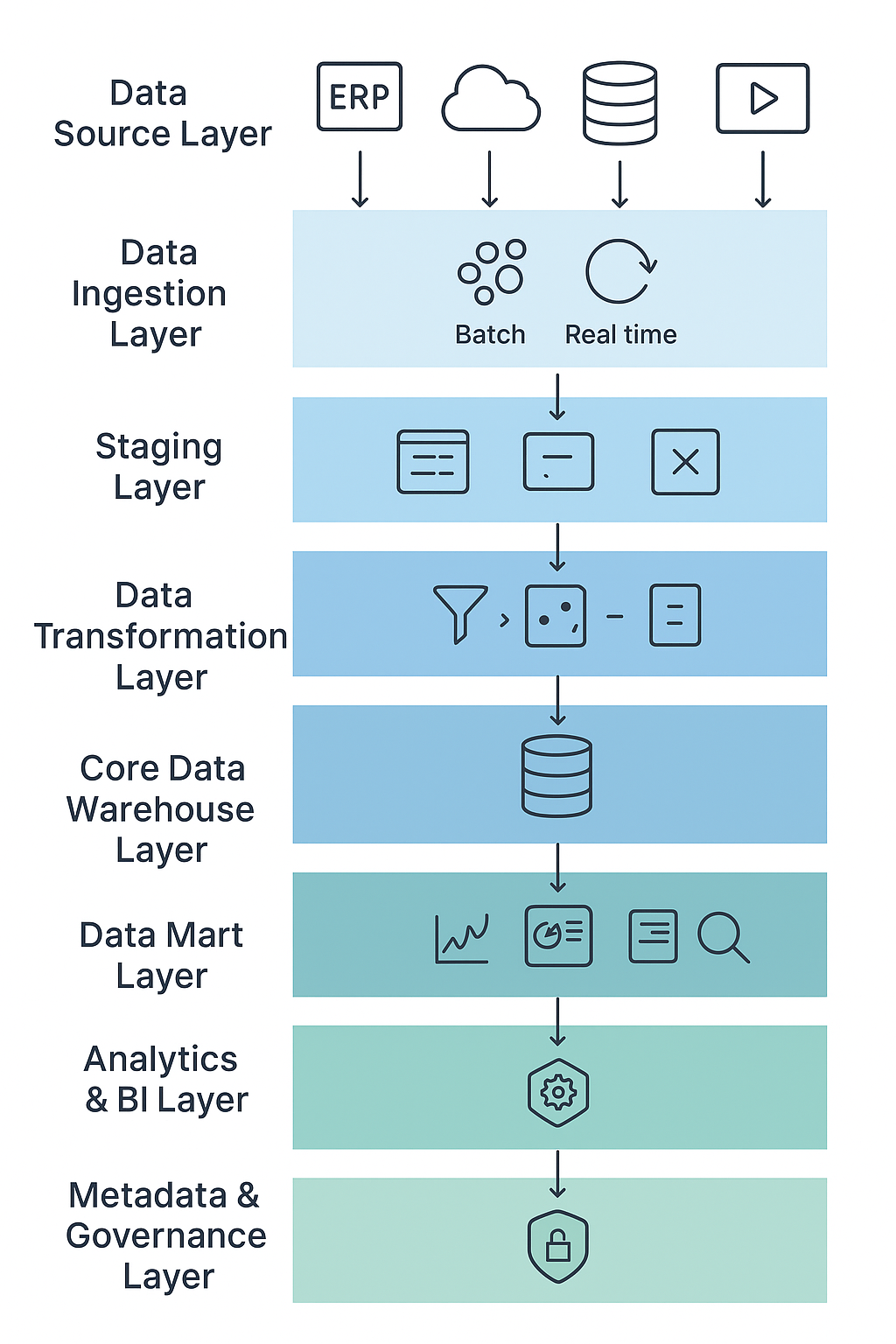
A modern EDW architecture typically consists of 9 logical layers.
1️⃣ Data Source Layer
This is where data originates.
Common Sources:
-
ERP systems (SAP, Oracle)
-
CRM platforms (Salesforce)
-
Transactional databases
-
IoT devices
-
Logs & events
-
Third-party APIs
📌 Key challenge: Different formats, structures, and refresh rates.
2️⃣ Data Ingestion Layer
This layer moves data from source systems into the warehouse.
Methods:
-
Batch ingestion (daily/hourly)
-
Real-time streaming
-
Change Data Capture (CDC)
Popular Tools:
-
Apache Kafka
-
AWS Glue
-
Azure Data Factory
-
Google Dataflow
-
Informatica
📌 A strong ingestion layer prevents data loss and duplication.
3️⃣ Staging Layer
Think of this as a temporary landing zone.
Purpose:
-
Hold raw data
-
Perform basic validation
-
Enable reprocessing if errors occur
📌 This layer protects your EDW from corrupt or incomplete data.
4️⃣ Data Transformation Layer (ETL / ELT)
This is where raw data becomes meaningful.
Tasks performed:
-
Data cleansing
-
Deduplication
-
Standardization
-
Business rule application
-
Data enrichment
ETL vs ELT:
-
ETL: Transform before loading
-
ELT: Load first, transform inside warehouse (cloud-native)
📌 Modern EDWs prefer ELT for scalability.
5️⃣ Core Data Warehouse Layer
This is the heart of the EDW.
Characteristics:
-
Structured data models
-
Historical data storage
-
Optimized for analytics
-
Strong schema design
Data Models:
-
Star Schema
-
Snowflake Schema
-
Data Vault (for large enterprises)
📌 This layer ensures consistent reporting across teams.
6️⃣ Data Mart Layer
Data marts are subject-specific subsets of the EDW.
Examples:
-
Sales Data Mart
-
Finance Data Mart
-
Marketing Data Mart
Benefits:
-
Faster queries
-
Simplified reporting
-
Department-level customization
📌 Data marts improve performance and usability.
7️⃣ Analytics & BI Layer
This is where business users interact with data.
Tools:
-
Power BI
-
Tableau
-
Looker
-
Qlik
-
Superset
Use cases:
-
Dashboards
-
KPI tracking
-
Ad-hoc analysis
-
Executive reports
📌 A good EDW makes analytics self-service.
8️⃣ Metadata & Governance Layer
This layer ensures control, compliance, and trust.
Includes:
-
Data lineage
-
Data catalogs
-
Quality rules
-
Access control
-
Compliance tracking (GDPR, HIPAA)
📌 Without governance, EDWs turn into data chaos.
9️⃣ Security & Access Layer
Security is not optional.
Key components:
-
Role-based access
-
Encryption (at rest & in transit)
-
Audit logs
-
Data masking
📌 Enterprises must protect sensitive business data at all times.
Modern EDW Architecture in the Cloud
Today’s enterprises are moving to cloud-native EDWs.
Popular Platforms:
-
Amazon Redshift
-
Google BigQuery
-
Snowflake
-
Azure Synapse Analytics
Advantages:
✔ Elastic scaling
✔ Lower infrastructure cost
✔ Faster deployment
✔ Built-in security
EDW vs Data Lake vs Lakehouse
| Feature | EDW | Data Lake | Lakehouse |
|---|---|---|---|
| Data Type | Structured | Raw | Mixed |
| Schema | Fixed | Schema-on-read | Flexible |
| Use Case | BI & reporting | ML & big data | Unified analytics |
📌 Many enterprises now combine EDW + Data Lake.
Common EDW Architecture Mistakes
-
Overcomplicated schemas
-
Ignoring data quality
-
No governance strategy
-
Poor performance tuning
-
Treating EDW as a dumping ground
Best Practices for EDW Architecture
✔ Design for scalability
✔ Automate data quality checks
✔ Separate compute & storage
✔ Document data models
✔ Enable self-service BI
✔ Monitor performance continuously
Business Benefits of EDW
-
Single source of truth
-
Faster reporting
-
Better forecasting
-
Improved compliance
-
AI & ML readiness
-
Higher business confidence
Enterprise Data Warehouse Architecture Diagram
FAQs
Q1. What is EDW architecture?
EDW architecture defines how enterprise data is collected, transformed, stored, and analyzed across the organization.
Q2. Is EDW still relevant in 2025?
Yes. EDW remains essential for trusted analytics, compliance, and executive reporting.
Q3. EDW or cloud data warehouse?
Modern EDWs are increasingly cloud-based for scalability and cost efficiency.
Q4. What industries use EDW?
Finance, healthcare, retail, telecom, SaaS, manufacturing, and government.
Q5. Can EDW support AI and ML?
Yes. Clean, historical data from EDW is crucial for AI models.
Final Thoughts
An Enterprise Data Warehouse is not just a database — it’s a strategic asset.
When designed correctly, EDW architecture turns raw data into clarity, confidence, and competitive advantage.
If your organization wants reliable analytics, faster decisions, and long-term scalability, investing in the right EDW architecture is no longer optional — it’s essential.

Leave a Reply