Production RAG Spring Boot Code Examples for RAG with Spring Boot (Real-World Patterns)
Most blogs show RAG with hello-world code.
Production systems fail because of missing structure, testing, and guardrails.
This article shows how RAG actually looks in real Spring Boot applications—with clean architecture, defensive coding, and cost awareness.
No hype. Just engineering.
Why “Production-Style” Matters in RAG
In real systems:
LLM calls are expensive
Retrieval can silently fail
Latency kills UX
Bugs don’t throw exceptions—they hallucinate
That’s why production RAG code must be:
Observable
Testable
Fail-safe
Cost-aware
Let’s build it properly.
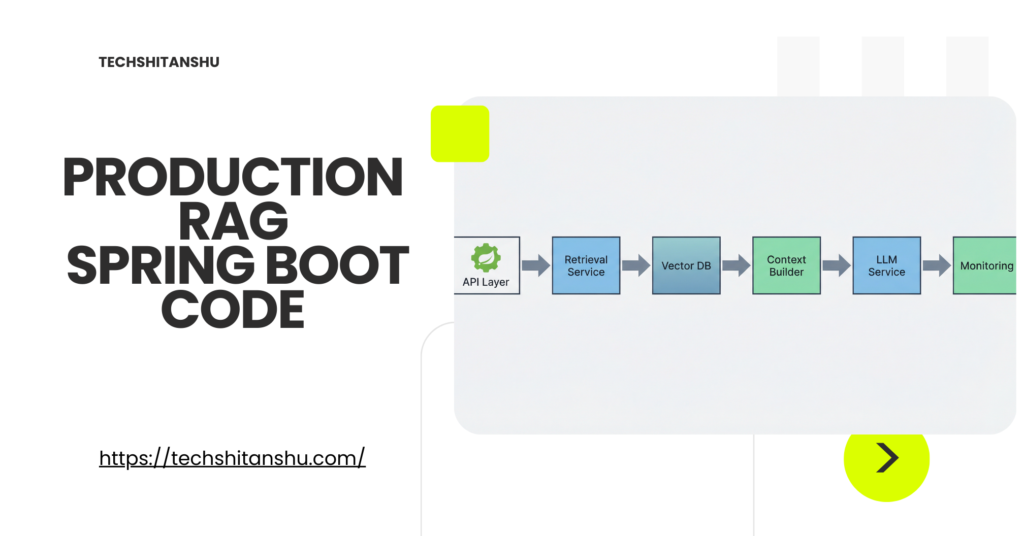
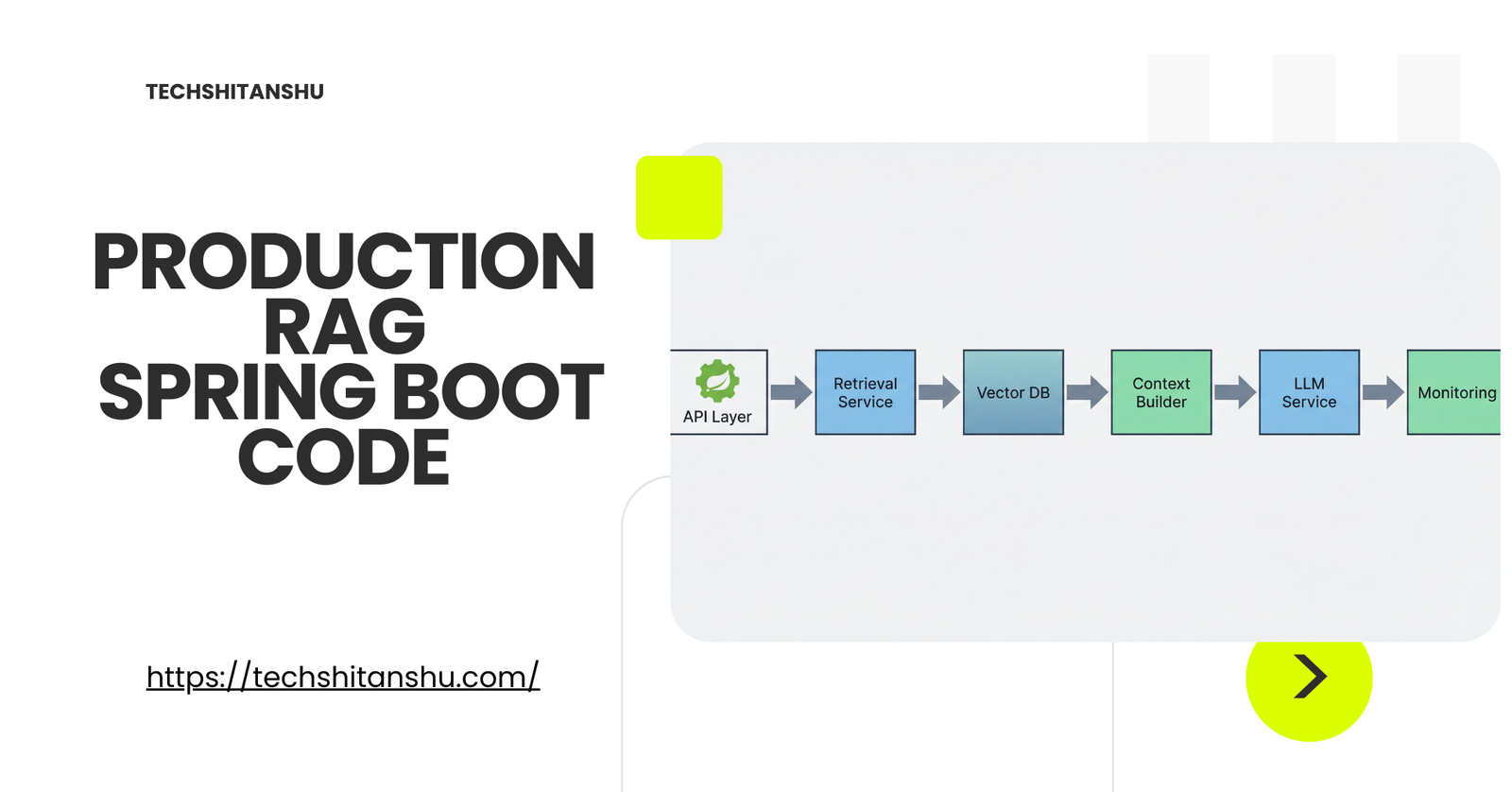
Reference Architecture (High Level)
Flow:
API → Query Service
→ Embedding
→ Vector Retrieval
→ Context Assembly
→ LLM Call
→ Response Validation
Each step is isolated, measurable, and replaceable.
1️⃣ Domain-First Design (Avoid God Services)
RAGRequest (Immutable)
public record RagRequest(
String question,
String userId,
Map<String, String> filters
) {}
Why this matters:
Clear contract
Easy to test
Prevents parameter explosion
2️⃣ Retrieval Layer (Fail Fast)
@Service
public class RetrievalService {
private final VectorStore vectorStore;
public RetrievalService(VectorStore vectorStore) {
this.vectorStore = vectorStore;
}
public List<Document> retrieve(RagRequest request) {
List<Document> docs =
vectorStore.similaritySearch(
request.question(),
4
);
if (docs.isEmpty()) {
throw new RetrievalEmptyException(
"No relevant context found"
);
}
return docs;
}
}
Why this is production-grade



 Context Assembly (Token-Safe)
Context Assembly (Token-Safe)
@Component
public class ContextBuilder {
private static final int MAX_CONTEXT_CHARS = 4_000;
public String build(List<Document> docs) {
StringBuilder context = new StringBuilder();
for (Document doc : docs) {
if (context.length() > MAX_CONTEXT_CHARS) break;
context.append(doc.getContent()).append("\n\n");
}
return context.toString();
}
}
Why this matters
Token limits enforced centrally
Prevents runaway cost
Keeps prompts predictable
4️⃣ Prompt Template (Explicit & Defensive)
@Component
public class PromptFactory {
public String create(String context, String question) {
return """
You are a backend assistant.
Answer ONLY using the context below.
If the answer is not present, say "I don't know".
Context:
%s
Question:
%s
""".formatted(context, question);
}
}
Production rule:
If the prompt allows guessing, the model will guess.
5️⃣ LLM Client (Abstracted & Measured)
@Service
public class LlmService {
private final ChatClient chatClient;
public LlmService(ChatClient chatClient) {
this.chatClient = chatClient;
}
public String generate(String prompt) {
return chatClient.call(prompt);
}
}
Why abstraction matters:
Easy provider swap
Easier testing
Cleaner metrics
6️⃣ Orchestrator (Thin, Testable)
@Service
public class RagService {
private final RetrievalService retrievalService;
private final ContextBuilder contextBuilder;
private final PromptFactory promptFactory;
private final LlmService llmService;
public RagService(
RetrievalService retrievalService,
ContextBuilder contextBuilder,
PromptFactory promptFactory,
LlmService llmService
) {
this.retrievalService = retrievalService;
this.contextBuilder = contextBuilder;
this.promptFactory = promptFactory;
this.llmService = llmService;
}
public String ask(RagRequest request) {
var docs = retrievalService.retrieve(request);
var context = contextBuilder.build(docs);
var prompt = promptFactory.create(context, request.question());
return llmService.generate(prompt);
}
}
Why this survives scale
No hidden logic
Each dependency mockable
Easy to profile & optimize
7️⃣ Controller (API-Safe)
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/rag")
public class RagController {
private final RagService ragService;
public RagController(RagService ragService) {
this.ragService = ragService;
}
@PostMapping("/ask")
public ResponseEntity<String> ask(
@RequestBody RagRequest request
) {
return ResponseEntity.ok(
ragService.ask(request)
);
}
}
8️⃣ Testing Retrieval (Real Vector DB)
@Test
void shouldRetrieveRelevantContext() {
vectorStore.add(
new Document("Spring Boot simplifies Java development")
);
var results =
vectorStore.similaritySearch("Spring", 1);
assertFalse(results.isEmpty());
}
✔ Real similarity
✔ No mocks
✔ Predictable behavior
9️⃣ Common Production Mistakes (Avoid These)
❌ Single giant service
❌ Calling LLM without retrieval checks
❌ No token limits
❌ Prompt logic inside controller
❌ No observability
What’s Next in the Series

Performance tuning & caching for RAG
Vector DB comparison for Java (Pinecone vs PGVector vs Redis)
Final Thought
If your RAG code looks simple, it’s probably fragile.
Production RAG is about:
Control
Visibility
Predictability
Not magic prompts.

Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
What is RAG (Retrieval-Augmented Generation) in simple terms?
RAG is an architecture where an LLM generates answers using external knowledge retrieved at query time (for example, from a vector database) instead of relying only on its training data.
Why use RAG instead of fine-tuning an LLM?
RAG is cheaper, faster to update, and safer. You can change your knowledge base without retraining models, making it ideal for enterprise and backend systems.
Is Spring Boot suitable for production RAG applications?
Yes. Spring Boot is well-suited for production RAG because it offers strong support for dependency injection, observability, testing, security, and scalability.
What role does Spring AI play in RAG systems?
Spring AI provides abstractions for LLMs, embeddings, and vector stores, allowing Java developers to build RAG pipelines without vendor lock-in or boilerplate code.
Which vector databases work best with Spring Boot RAG?
Popular options include Pinecone, Weaviate, Milvus, and PGVector. The best choice depends on scale, latency requirements, and deployment model.
How do you prevent hallucinations in RAG pipelines?
Hallucinations are reduced by enforcing strict retrieval checks, limiting context size, and using defensive prompt templates that instruct the model to answer only from provided context.
How expensive is running RAG in production?
Costs depend on embedding generation, retrieval frequency, and LLM token usage. Production systems reduce cost using caching, token limits, and selective retrieval.
Can RAG pipelines be tested automatically?
Yes. You can test retrieval logic using Testcontainers with real vector databases and validate prompt behavior with controlled inputs.
Is RAG useful for interview preparation and system design discussions?
Absolutely. RAG is now a common topic in senior backend, system design, and AI interviews—especially for Java and microservices roles.
When should you avoid using RAG?
RAG may be unnecessary for simple chatbots, static FAQs, or cases where the LLM already has sufficient general knowledge.

Leave a Reply