Service Mesh Explained: A Powerful Guide to Secure, Observable Microservices at Scale
Modern applications are no longer built as one big system. They’re broken into dozens or hundreds of microservices, each talking to each other constantly.
And that’s exactly where things start to break down.
- How do you secure service-to-service traffic?
– How do you observe failures across services?
– How do you manage retries, timeouts, and traffic policies without rewriting code?
That’s where Service Mesh comes in.
This guide explains what a Service Mesh is, why it matters, how it works, and when you should (or shouldn’t) use one — in a way that actually makes sense.
What Is a Service Mesh?
Modern applications are no longer built as one big system. They’re broken into dozens or hundreds of microservices, each talking to each other constantly.
And that’s exactly where things start to break down.
- How do you secure service-to-service traffic?
– How do you observe failures across services?
– How do you manage retries, timeouts, and traffic policies without rewriting code?
That’s where Service Mesh comes in.
This guide explains what a Service Mesh is, why it matters, how it works, and when you should (or shouldn’t) use one — in a way that actually makes sense.
Why Service Mesh Exists (The Real Problem)
As microservices grow, teams struggle with:
🔒 Securing service-to-service communication
📉 Debugging failures across services
🔁 Implementing retries, timeouts, circuit breakers
📊 Getting consistent metrics and tracing
⚙️ Managing traffic for canary or blue-green deployments
Doing this inside every service leads to:
Code duplication
Inconsistent behavior
Slower development
A service mesh moves all of this out of your code.
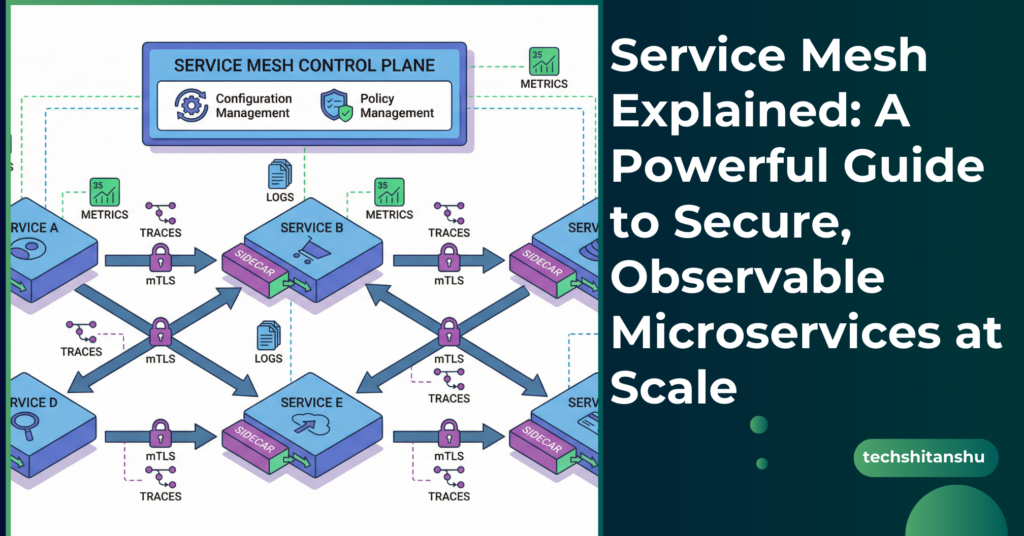
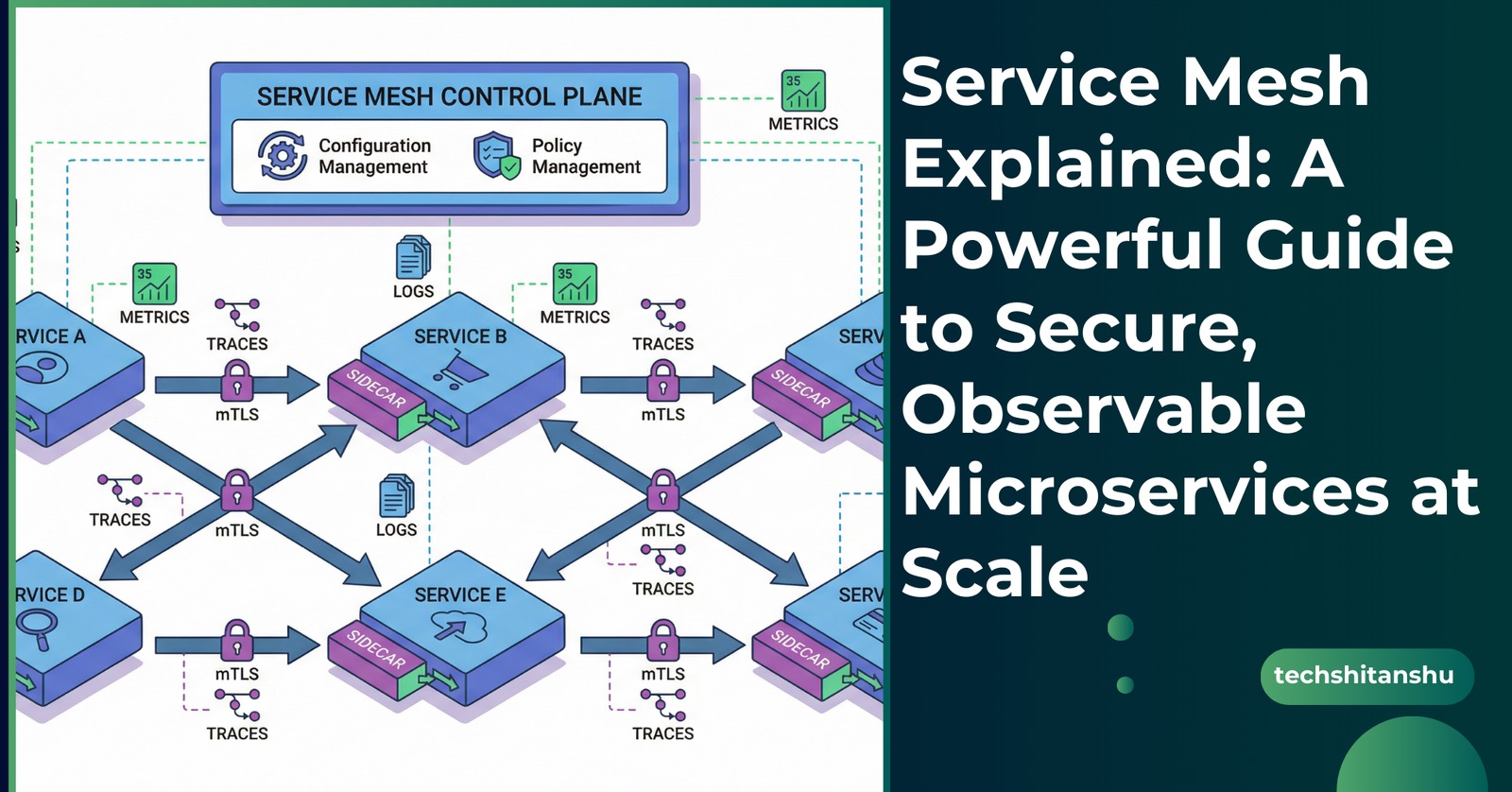
How Service Mesh Works (Architecture Overview)
A Service Mesh works using a sidecar proxy model.
Core Components
Data Plane
Lightweight proxies (usually Envoy)
Deployed alongside each service
Intercepts all inbound and outbound traffic
Control Plane
Manages configuration, policies, and certificates
Pushes rules to the proxies
Your application never talks directly to another service — the proxy does.
Key Capabilities of a Service Mesh
1️⃣ Zero-Trust Security (mTLS)
Automatic mutual TLS between services
Identity-based authentication
No app-level certificates required
2️⃣ Traffic Management
Retries, timeouts, circuit breakers
Canary deployments
Traffic mirroring and splitting
3️⃣ Observability
Distributed tracing
Service-level metrics
Request-level visibility
4️⃣ Policy Enforcement
Rate limiting
Access control
Compliance rules
All of this works without changing application code.
Popular Service Mesh Tools
| Service Mesh | Best For |
|---|---|
| Istio | Enterprise-grade control & security |
| Linkerd | Simplicity, low overhead |
| Consul Connect | HashiCorp ecosystem |
| AWS App Mesh | AWS-native workloads |
Service Mesh vs API Gateway
| Aspect | Service Mesh | API Gateway |
|---|---|---|
| Scope | Internal service traffic | External client traffic |
| Layer | East–West | North–South |
| Security | mTLS between services | Auth, rate limiting |
| Use case | Microservices networking | Public APIs |
👉 They complement each other, not replace.
When You SHOULD NOT Use a Service Mesh
Service Mesh is powerful — but not always necessary.
Avoid it if:
You have fewer than ~5 microservices
Your traffic patterns are simple
Your team lacks Kubernetes maturity
You don’t need advanced security or observability
A service mesh introduces operational complexity — use it intentionally.
Real-World Use Cases
✔ Large Microservices Platforms
Netflix, Uber, and Airbnb use service mesh concepts for:
Resilience
Security
Traffic control
✔ Regulated Industries
Finance and healthcare use service mesh for:
Encryption everywhere
Auditability
Compliance
✔ Platform Engineering Teams
Internal developer platforms rely on service mesh to:
Standardize networking
Reduce developer burden
Cost & Performance Considerations
Service Mesh adds:
Extra CPU & memory (sidecars)
Operational overhead
Learning curve
But it saves long-term cost by:
Preventing outages
Improving debugging time
Standardizing security
Service Mesh in Simple Terms
Think of Service Mesh as:
Kubernetes networking with a brain
It gives you control, visibility, and safety over how services talk — at scale.
Final Takeaway
Service Mesh is not a trend — it’s a maturity milestone.
If you’re building:
Large microservices systems
Security-sensitive platforms
Cloud-native infrastructure at scale
Then a service mesh can dramatically improve reliability, visibility, and developer experience.
FAQ
What is a service mesh in microservices?
A service mesh is an infrastructure layer that manages communication, security, and observability between microservices without modifying application code.
Is Istio a service mesh?
Yes. Istio is one of the most popular and powerful service mesh implementations, offering advanced traffic management, security, and observability.
Do I need a service mesh for Kubernetes?
Not always. Kubernetes works fine without a service mesh. You should use one only when you need advanced networking, security, and observability at scale.
What problem does a service mesh solve?
It solves service-to-service security, traffic control, observability, and reliability issues in large microservices systems.
Does a service mesh replace an API gateway?
No. A service mesh manages internal traffic, while an API gateway handles external client requests. They are complementary.

Leave a Reply