Testing RAG Pipelines in Spring Boot (The Right Way)
Testing Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) systems is not the same as testing REST APIs or services.
RAG systems are:
Non-deterministic
Data-dependent
Cost-sensitive
Multi-stage pipelines
If you try to test them like normal services, you’ll either:
Write brittle tests, or
Skip testing entirely
This article explains how Java teams test RAG pipelines in Spring Boot in a way that is reliable, fast, and production-safe.
Why RAG Testing Is Hard
Traditional backend tests expect:
Deterministic inputs
Deterministic outputs
RAG breaks this assumption.
Challenges include:
LLM responses vary
Retrieval results depend on embeddings
Vector similarity is approximate
External APIs are slow and costly
Solution:
You don’t test “the answer”.
You test each stage of the pipeline.
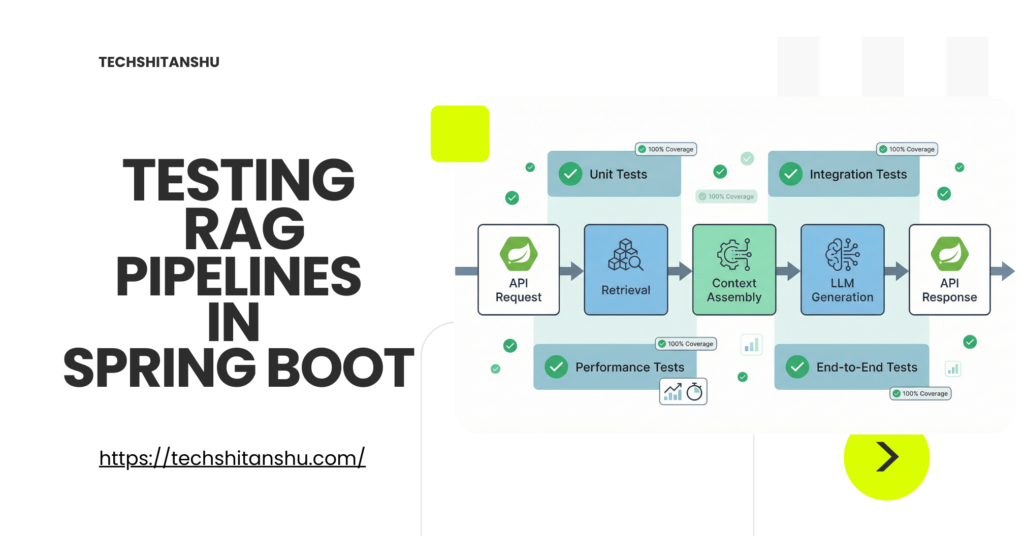
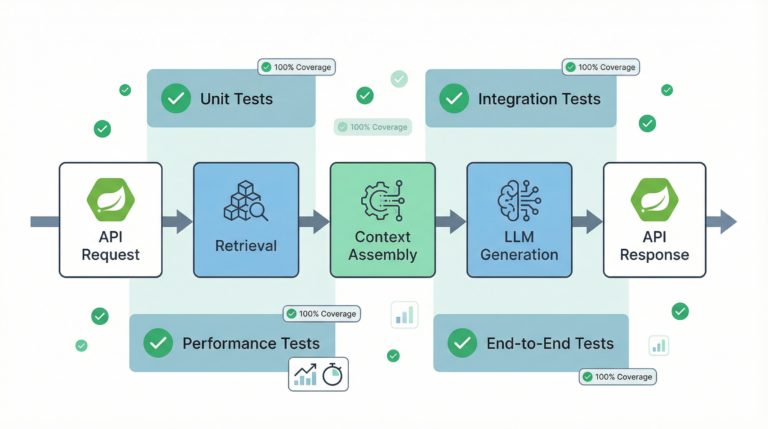
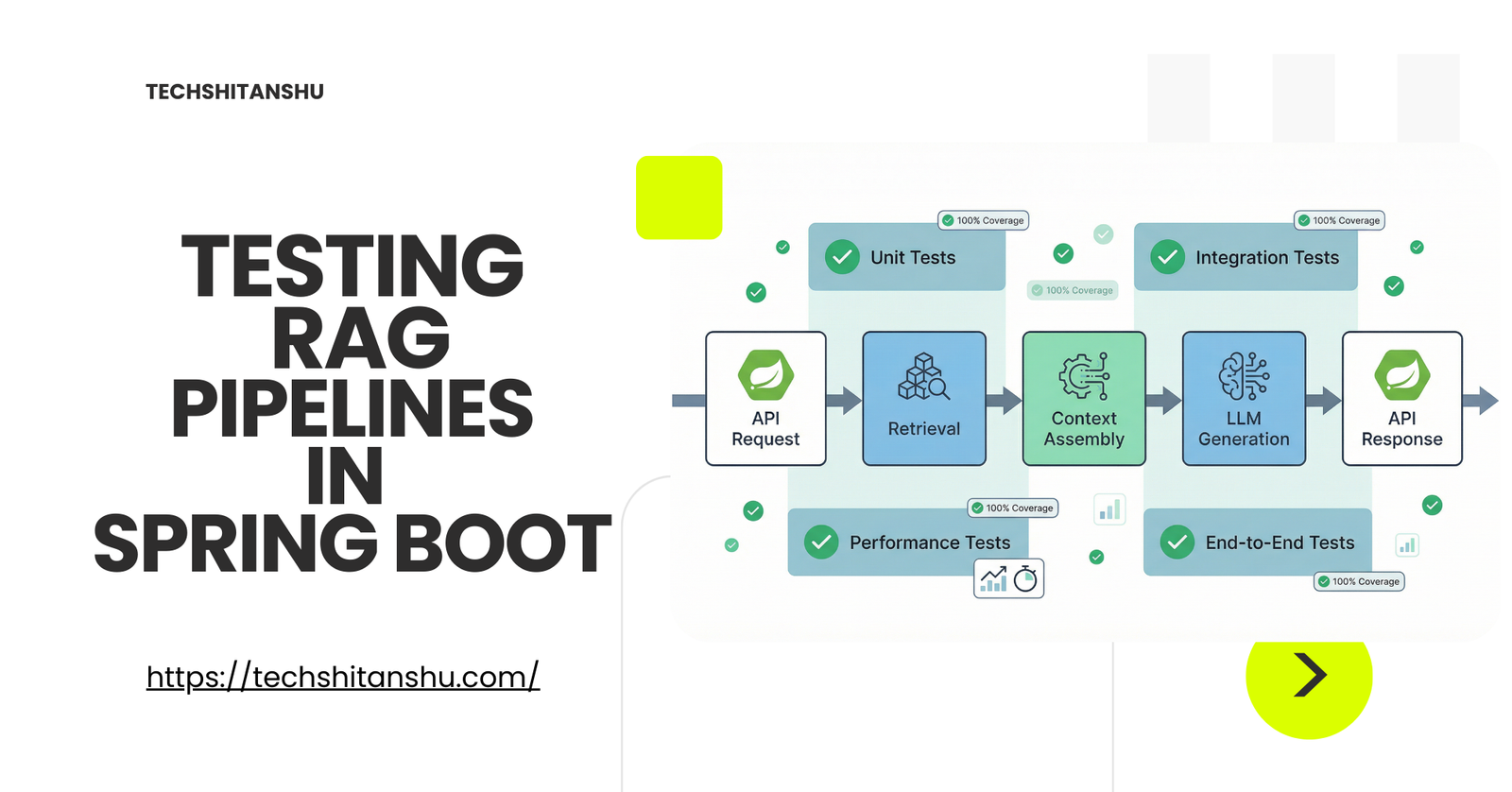
The RAG Pipeline (What to Test)
A typical RAG pipeline has 5 testable layers:
Chunking & ingestion
Embedding generation
Retrieval correctness
Prompt construction
Response handling
Each layer is tested independently.
1️⃣ Testing Document Chunking & Ingestion
What You Test
Documents are split correctly
Metadata is preserved
Chunks are stored once (not duplicated)
What You Don’t Test
Embedding quality
LLM output
Example Test
@SpringBootTest
class DocumentIngestionTest {
@Autowired
private DocumentIngestionJob ingestionJob;
@Autowired
private VectorStore vectorStore;
@Test
void shouldIngestAndStoreChunks() {
ingestionJob.ingest(List.of("Spring Boot makes Java simple."));
var results = vectorStore.similaritySearch("Spring", 1);
assertFalse(results.isEmpty());
}
}
✅ Verifies ingestion pipeline
❌ Does NOT call an LLM
2️⃣ Testing Embedding Generation (Mocked)
You never test real embedding APIs in unit tests.
Instead:
Mock embedding clients
Use deterministic vectors
Why
Fast tests
No token cost
Stable results
Example
@ExtendWith(MockitoExtension.class)
class EmbeddingServiceTest {
@Mock
private EmbeddingClient embeddingClient;
@Test
void shouldReturnEmbeddingVector() {
when(embeddingClient.embed("test"))
.thenReturn(List.of(0.1, 0.2, 0.3));
List<Double> embedding = embeddingClient.embed("test");
assertEquals(3, embedding.size());
}
}
3️⃣ Testing Retrieval Correctness (Critical)
This is the most important RAG test.
You are testing:
“Does the right context get retrieved for a query?”
Strategy
Use a test vector store (in-memory)
Insert known documents
Assert retrieval order or presence
Example
@SpringBootTest
class RetrievalTest {
@Autowired
private VectorStore vectorStore;
@Test
void shouldRetrieveRelevantDocument() {
vectorStore.add(new Document("Spring Boot simplifies Java"));
vectorStore.add(new Document("Kubernetes manages containers"));
var results = vectorStore.similaritySearch("Spring", 1);
assertEquals("Spring Boot simplifies Java",
results.get(0).getContent());
}
}
✅ Tests semantic grounding
❌ Does NOT test generation
4️⃣ Testing Prompt Construction (Very Important)
Prompt bugs cause:
Hallucinations
Security issues
Incorrect answers
Prompts must be testable artifacts.
What You Test
Context is injected
Instructions are present
No empty prompts
Example
class PromptTemplateTest {
private final PromptTemplate promptTemplate = new PromptTemplate();
@Test
void shouldBuildPromptWithContext() {
String prompt = promptTemplate.create(
Map.of("context", "Spring Boot docs",
"question", "What is Spring Boot?")
);
assertTrue(prompt.contains("Spring Boot docs"));
assertTrue(prompt.contains("What is Spring Boot?"));
}
}
✅ Prompt logic is deterministic
❌ Output quality is not tested
5️⃣ Testing the RAG Service (LLM Mocked)
You never hit a real LLM in CI.
You mock the LLM response and test:
Pipeline wiring
Flow correctness
Error handling
Example
@ExtendWith(MockitoExtension.class)
class RagServiceTest {
@Mock
private ChatClient chatClient;
@Mock
private VectorStore vectorStore;
@InjectMocks
private RagService ragService;
@Test
void shouldReturnAnswerFromLLM() {
when(vectorStore.similaritySearch(any(), anyInt()))
.thenReturn(List.of(new Document("Spring context")));
when(chatClient.call(anyString()))
.thenReturn("Spring Boot is a framework");
String answer = ragService.answer("What is Spring Boot?");
assertTrue(answer.contains("Spring Boot"));
}
}
✅ Tests orchestration
❌ Does NOT test model intelligence
6️⃣ End-to-End Tests (Optional, Controlled)
End-to-end tests are:
Slow
Expensive
Flaky
Use them sparingly.
Best Practices
Run nightly, not per commit
Use strict token limits
Log prompts & responses
Never assert exact text
Example Assertion
assertTrue(response.length() > 20);
assertFalse(response.contains("I don't know"));
7️⃣ What NOT to Test in RAG Systems
❌ Exact wording of responses
❌ Creativity or tone
❌ Model “intelligence”
❌ Token-level outputs
These change across:
Models
Versions
Providers
Recommended RAG Testing Strategy (Summary)
| Layer | Strategy |
|---|---|
| Chunking | Unit tests |
| Embeddings | Mocked |
| Retrieval | In-memory vector store |
| Prompts | Deterministic tests |
| LLM calls | Mocked |
| E2E | Limited & controlled |
Interview Insight (Important)
If asked:
“How do you test RAG systems?”
Correct answer:
“We don’t test the AI’s creativity.
We test retrieval correctness, prompt integrity, and pipeline wiring.”
This signals real-world experience.
What’s Next in the Series
Performance tuning & caching for RAG
Vector DB comparison for Java (Pinecone vs PGVector vs Redis)
Final Thoughts
RAG testing is about trusting the pipeline, not the model.
Spring Boot makes this easier because:
Clear layers
Dependency injection
Strong testing ecosystem
If your RAG pipeline is well-tested, model changes become safe—and that’s the real goal.

FAQ
Why is testing RAG pipelines different from testing normal APIs?
RAG pipelines depend on retrieval quality, embeddings, and LLM behavior. Testing must validate both data retrieval and prompt-to-response flow, not just HTTP responses.
Can RAG pipelines be tested without mocking everything?
Yes. Production-grade testing uses real vector databases via Testcontainers while mocking only the LLM layer to keep tests deterministic.
What should be tested first in a RAG system?
Start with retrieval accuracy. If the wrong documents are retrieved, the LLM output will be unreliable regardless of prompt quality.
How do you test prompt correctness in Spring Boot?
Prompt templates are tested by asserting structure, context injection, and token limits rather than exact text responses.
Is Testcontainers suitable for AI workloads?
Absolutely. Testcontainers allows you to run Pinecone alternatives, Weaviate, Milvus, or PGVector locally, ensuring retrieval logic behaves like production.
Should LLM responses be asserted exactly in tests?
No. Production tests should validate response intent, structure, or confidence thresholds—not exact wording.
How does testing reduce hallucinations in RAG systems?
Testing enforces retrieval validation, context limits, and fallback logic, preventing the LLM from answering without verified knowledge.
Is RAG testing important for interviews and system design discussions?
Yes. Senior and staff-level interviews increasingly expect candidates to explain how AI pipelines are tested, monitored, and validated.

Leave a Reply